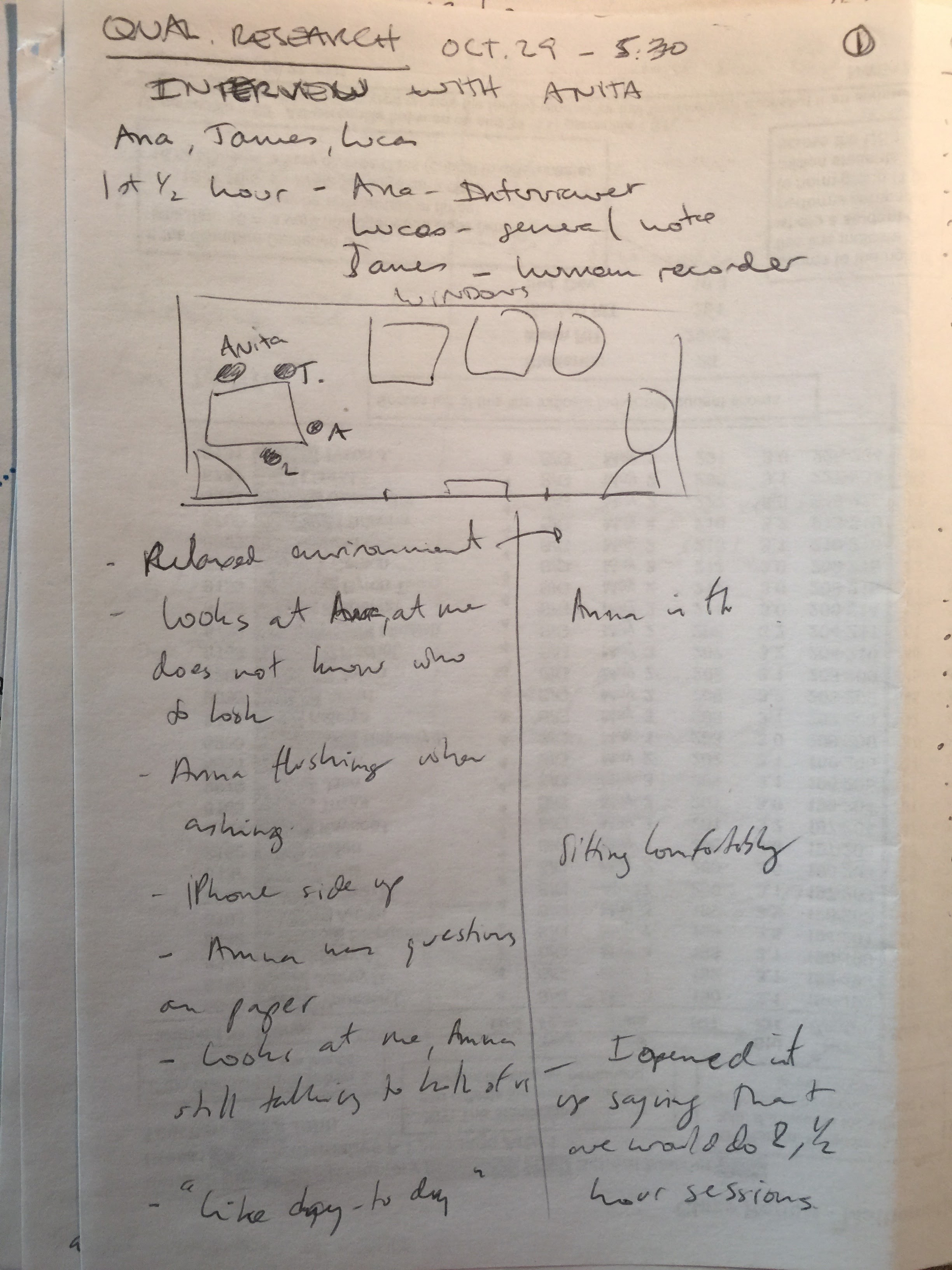
Raw Notes:
Arquivo da categoria: LDT – GSE – Stanford
Tech 4 Learners – Week 6 – Class Notes
Qualitative Research – Week 6 – Class Notes
Qualitative Research – Week 6 – Reading Notes
Assignment
Making Sense of the Data
- Taylor, S., & Bogdan, R. (1998). “Working With Data,” Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods. (Third Edition). New York: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 134-160.
- Charmaz, K. (1983). “The Grounded Theory Method: An Explication and Interpretation,” In R. Emerson (Ed.) Contemporary Field Research: A Collection of Readings. Boston: Little, Brown. pp. 109-126.
- Graue, M. E., & Walsh, D. (1998). Studying Children in Context: Theories, Method, and Ethics. Thousand Oaks: Sage. pp. 201-206.
Ricky in Town
Qualitative Research – Tech Adoption – Group Meeting
Had our group meeting and decided upon our questions to ask Anita:
Background (introductory icebreakers)
- Thank you for letting us observe the event – how did it go for you?
Grand tour questions
- In your own words, what does SVEF do?
- Tell us about your specific responsibilities as iHub Manager at SVEF.
- Walk us through a typical day as iHub Manager at SVEF.
Program Specifics
- What’s the process that startups go through with iHub prior to pitch night?
- Prior to orientation?
- After orientation?
- To what extent is iHub involved after orientation?
- What other events/resources do you provide with similar goals/priorities?
Tech 4 Learners – Week 6 – OMS Visit
Went to OMS today to test our prototype with “A”. Successful in a way yet not ground breaking. We were able to have him interact with our prototype yet only a few events of spontaneous word generation. We recorded the entire session and from it we will be able to extract some more information about the specific triggers for this generation of words. Word repetition and generation when prompted was not a problem.
After the testing session we interviewed Marina and the feedback was that this kind of prompt to comment has been applied on him for the past years with limited success. He has shown gains yet we still have to think outside of the box to find some way for him to generate words and transfer this ability to his daily activities. Something that would be practical and promote a degree of independence for him.
Learning Environments – Week 6 – Class Notes
Great exercise in the morning to classify our projects into categories and learning theories… we had to self-organize and create the labels on the header row and column of the chart then discussed it.

Then the reading Czars organized a really interactive session where each group had to create a game, present it to the class by only showing it in action – not telling what the rules were – to feel what the book touched upon: a private language, exclusive, your own secret, fun to watch and so on 🙂 Great job!
Second half of class we had a Skype call with the author of Kisisi (Our Language) – amazing opportunity. Unfortunately I had to leave early to go test the prototype for Tech4Learners.

Learning Environments – Week 6 – Observations/Interviews of a Tech Learning Environment 2
Project Assignment:
EDUC 333A – Paper Two
Observations/Interviews of a Tech Learning Environment
Lucas Longo
How do you learn from Einstein?
Wouldn’t it be great if you could travel back in time to convince Einstein to publish an online course, using all of our current technology? What challenges might he face in creating this course? How do the tools aid or hinder him in organizing and sharing his knowledge? How good of a learning experience would it be? How much would I actually learn from it?
Fun fact: Einstein has a mathematics and physics teaching degree from Zürich Polytechnic.
I decided to investigate the process of sharing expert’s knowledge using the currently available online/digital toolset and how can best-practices, current research findings and methodologies be incorporated into this process. My ‘experts’ are non-academia, industry professionals and practitioners who’s knowledge would be worth sharing. The range I am thinking about goes from a high-tech CEO to a local farmer with deep knowledge about a specific local crop.
How can we provide technology, tools and motivation for these experts to share their knowledge? How do we organize the course delivery mechanisms to maximize reach and not sacrifice effective, long-lasting learning? Is technology not providing the adequate tools? Is it a matter of access or content quality?
I identified some problem areas:
- Motivational
- How to motivate experts to share their knowledge?
- How to motivate learners to acquire new knowledge?
- Pedagogical
- Do experts have the right skills to share their knowledge?
- Do learners have the right methods and discipline to absorb new knowledge?
- Mechanical
- Are the tools available for expert to share their knowledge adequate?
- Are the tools available for learners to acquire knowledge adequate?
- Access
- How easily can experts access the available tools?
- How easily can learners access knowledge through the available tools?
Initially I was hoping to observe qualitatively a teacher creating content for an online course. By creating I mean recording video, preparing examples to show in class, designing the lesson plan and any other stage of the creation process. Unfortunately the opportunity did not present itself and I also realized that to schedule an observation of this process happening in the time frame I had would be impossible.
I rerouted my strategy towards research and interviews.
Maybe I could catch a glimpse of the impact educational technology has had in teaching practices at Stanford. Get input from the experts about what their experience have shown them and what are the tendencies. I had the honor of being introduced to and interview Candace Marie Thille, Anna Porteus, and Sarah Rutherford-Quach.
The method I adopted in the interview was to start with the description of what I was interested in observing and ask about their experiences in this arena to start to “make words fly” (Glesne & Peshkin, 1992). I prepared some overarching questions to guide me in terms of general topics but I knew I would not follow them directly – I felt this first round of interview should be more exploratory in order to inform me about what are the general feelings on the topic and where the current field of research is pointing towards. During the interview I took notes and decided not to record the audio to maintain an informal aspect to the interview.
What follows are the questions that guided me through the interview followed by my amended notes and a summary of what I got most out of the interview.
Interview Questions:
- How do you use online tools to teach your courses nowadays?
- How have the online tools changed your role as a teacher?
- Where do you see the online tools falling short?
- Which tools do you use for the content creation?
- What is you preferred method of teaching?
- Do online learning tools provide a better learning experience for learners?
- How have the tools evolved over time?
- What do you see are next steps in the evolution of online learning?
- How has the role and work of teachers changed because of these tools?
Interview with Candace Thile & Anna Porteus:
Oct. 20, 2015 from 5:30pm to 6:15pm at Candace’s office at the Barnum Center, Stanford
Content production:
- To produce content for online courses they use mostly slides.
- Do not do video lectures.
- Voice over animations to illustrate concepts
- Students or third party create them on demand.
Challenges of online courses:
- How to get learner involved.
- How to get started.
- How to get learners engaged.
- Need highly motivated learners for actual course completion.
Flipping the classroom:
- Nothing extremely new.
- Read text books at home and discuss in class.
- Hybrid Distance Learning and Computer Based Distance Learning more appropriate.
Canvas:
- It’s not an LMS, it a MMS – Material Management System.
- Single sign on is good.
- Harder to creta bookmarks.
- Good with announcements.
- Statistics about students not as good.
- No open text search of the content.
Learning outcomes:
- Instructor feedback is very important.
- Online assessment is enough usually.
Teaching Style:
- Practice material was all given by and graded by the TA.
- Now material is all online.
- Much more group work.
- Teacher is much more a facilitator.
Anna
Education Technologies:
- Excessive drive towards market share.
- Design for sub-optimality to satisfy the market: make it easier.
- How to do it? A lot of research still has to be done.
Companies:
- Scaffolding:
- No instruction on how to create a “good enough” curriculum.
- No ‘holding hands’ along the process for those who have never done it.
- Platform has to scaffold you on thinking about the results.
- Guide faculty towards activities
Recommended further research:
- Evidence Based Learning
- Hebert Simon
Summary (Candace & Ann)
- Creating the content is not the hard part. Slides will be enough 99% of the time.
- Hard to keep learners engaged over time on online courses.
- Learning curve to use ed-tech tools is not a problem.
- LMS is used mostly as a content organizer.
- Tools in general lack scaffolding for good pedagogy.
Interview with Sara Rutherford-Quach
Oct. 27, 2015 from 4:30pm to 5:15pm at the ELL Offices, Stanford
Teacher’s Role:
- Transitioned from classroom teacher to MOOC reluctantly.
- How to maintain classroom conversations in a MOOC?
Personal Experience:
- c-Mooc & team oriented.
- Hot to get people to share knowledge.
- Assignments involved collection evidence of work and submitting.
- Peer reviews were part of the assignment.
NovoEd:
- Hybrid models have better outcomes – single digit vs. 80+% completion rates.
- Teaching videos used instead of video lectures – there were a problem with students.
- Hard to record real examples of good in-class teaching.
- Online teams would end up with 2 or 3 peers.
- Highly recommended that people would take the courses in groups in one physical location, regularly.
Sharing Knowledge in Corporate Environment:
- Would have to be designed into job description.
- Culture of company to learn in groups.
Further research:
- Professional Development: look at Jeff Zwier’s work: http://www.jeffzwiers.org
- Jonathan Osborne: course design and interaction.
Summary (Sara)
- Good results only when human interaction is present.
- Groups, peer support, and teacher feedback are essential.
- Hard to capture on video good examples of research recommendations being applied.
- Dropout rates on online only courses are absurd.
- Without human contact, online learning might not happen effectively.
Following the interviews I would be at a better position to research effectively the subject matter with suggested references, correct terminology and preconceptions dispelled. The research started out on Google and LinkedIn Slides to find summarized information about the macro concepts and then migrated to searching in Google Scholar for research papers. I also focused on relatively recent research (within the past 10 years) to ensure that the technologies researched were relatively current. This proved to be the most effective way to getting a good breadth about what has been done and observed as well as pointing me towards several areas I did not even know existed. It was a truly awe inspiring, jaw-dropping and humbling experience.
Research Findings:
“While students rated the instructors very positively, the results also indicate that instructors still need to have their roles transformed pedagogically, socially, and technologically if they are to establish a more engaging and fruitful environment for online learning.”
- Liu, X., Lee, S., Bonk, C., Su, B., Magjuka, R. (2005). Exploring Four Dimensions of Online Instructor Roles: A Program Level Case Study. Online Learning Consortium
- http://onlinelearningconsortium.org/sites/default/files/v9n4_liu_1.pdf
“This study found a change in the beliefs and teaching presence of the instructors from their initial resistance to online teaching to an approach which is mindful of the student experience and promotes a dialogical approach to online learning.”
- Redmond, P., (2011) From face-to-face teaching to online teaching: Pedagogical transitions. ascilite 2011 Hobart:
- http://www.ascilite.org/conferences/hobart11/downloads/papers/Redmond-full.pdf
“In spite of the proliferation of online learning, creating online courses can still evoke a good deal of frustration, negativity, and wariness in those who need to create them.”
- Vai, M. & Sosulski, K. (2015). Essentials of Online Course Design. A Standards-Based Guide, 2nd Edition. Routledge
- https://www.routledge.com/products/9781138780163
“Technology alone does nothing to enhance online pedagogy. According to Jacobsen, et al. (2002), the real challenge is to “develop fluency with teaching and learning with technology, not just with technology, itself” (p.44).”
- Keengwe, J. & Kidd, T. (2010). Towards Best Practices in Online Learning and Teaching in Higher Education. MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching
- http://jolt.merlot.org/vol6no2/keengwe_0610.htm
Conclusions:
In general, my research has shown me that there are several types of online education and that each has its strengths and weaknesses and are used in different contexts. Not only subject matter influences the type of course utilized but mostly the educator leads the way in terms of structure, level of interaction and potential for learner engagement and course completion.
I also learned that the technology is not the barrier to effective online learning. The method is. Even thought there is no silver bullet or definite method, one thing seems to be clear to me – human contact is essential – the more of it that is designed into the online education, the more effective the learning experience is. Open schedule online learning style require a highly motivated learner since peer or instructor support is minimal. Hybrid distance learning and Computer Based Distance learning styles, which offer more human contact with the instructors and the peers, seem to have the best effectiveness in terms of actual long-term learning.
In terms of the learning theories discussed in class, I can see a little of each when looking at online education. Montessori’s ‘learn by doing’ certainly applies to effective online learning. In other words, it is no use simply uploading videos online of lectures, one must plan the online learning experience to integrate assignments, discussions and work submissions to hopefully obtain some success in learning. With little or no interactive activities, discussions, practice, or communication with peers, it seems like online education is as good as watching television.
One issue I find baffling in online education, is how do you determine the student’s level when starting the course. Surely you can specify prerequisites and state what the learner should know before starting the course yet ascertaining the adequacy of the student coming into an online course is surely a much more imprecise matter.
During the course it is also harder to evaluate a learner’s needs online as opposed to in a classroom setting. Therefore, applying Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development is much harder online. Peer-review and peer-support could supplement this structural limitation on online courses yet one-to-one human interaction is hard to supplant. “What the child is able to do in collaboration today he will be able to do independently tomorrow” (Vygotsky, 1934/1987). How do we achieve that with online learning? “By giving our students practice in talking with others, we give them frames for thinking on their own.” Vygotsky, 1978).
These two phrases seem to sum up my first impressions with this exercise – it seems to be much more natural and effective for us to learn from another human being. Granted that it is possible to learn simply by reading a book or taking an online course with no human intervention, yet the motivational level, interest level and dedication required to learn is orders of magnitude greater that having someone lead you through the process, guide you towards your own understanding, facilitating your comprehension, and scaffolding you towards expertise.
So how do you learn from Einstein? Going back to the ‘problem areas’ I identified at the beginning of this paper, we might be able to say the following:
- Motivational: You and him have to be motivated and committed for it to happen.
- Pedagogical: He needs to figure out how to explain it to you and you have to make an effort to make sense of it.
- Mechanical: The tools have to offer adequate interactions and affordances for content creation and consumption.
- Access: You must be able to access not only the content but Einstein himself as well as your peers who are taking the course at the same time you are.
Learning Environments – Week 6 – Interview
For the assignment “Observations/Interviews of a Tech Learning Environment Paper #2” I interviewed Sara Rutheford-Quach
Take-aways:
- Human interaction is necessary – be it teacher-student or student-student
- Motivation is not a problem for higher-ed teachers
- Tools do their job
- Hard to train the teachers
Notes: