The Research Methods Knowledge Base: 3rd edition by William M.K. Trochim and James P. Donnelly. Chapter 1
- 1-1 The Language of Research
- 1-1a Types of Studies (Cumulative)
- Descriptive
- Relational: two variables
- Causal: most demanding
- Evidence-based practice
- 1-1b Time in Research
- Cross-sectional – single point in time
- Longitudinal studies – over time
- Repeated measures
- Two or a few waves of measurement
- Time series
- Over 20 waves of measurement
- Repeated measures
- 1-1c Type of Relationships
- Simple correlational relationship – act in synchrony
- Causal relationship – one explains another
- Third-Variable problem – something else which affects both variables
- Patterns
- No relationship
- Positive relationship
- Negative relationship
- 1-1d Variables
- Attributes
- Dependent / Independent
- Exhaustive: holds all possible values
- Mutually exclusive: employed, not employed + 2nd job
- 1-1e Hypotheses
- Prediction, in concrete terms
- Not all research has a hypothesis – exploratory
- Alternative hypothesis
- Null hypothesis
- One-tailed hypothesis
- 1-1f Types of Data
- Quantitative & Qualitative
- “All quantitative data is based upon qualitative judgements; and all qualitative data can be described and manipulated numerically.” (Trochim & Donnely, 2006)
- Quantitative & Qualitative
- 1-1f The Unit of Analysis
- Individuals, Groups, Artifacts, Geo, Social
- 1-1h Research Fallacies
- Ecological fallacy – group stereotyping
- Exception fallacy – one does not represent the group
- 1-1a Types of Studies (Cumulative)
- 1-2 Philosophy of Research
- 1-2a Structure of research
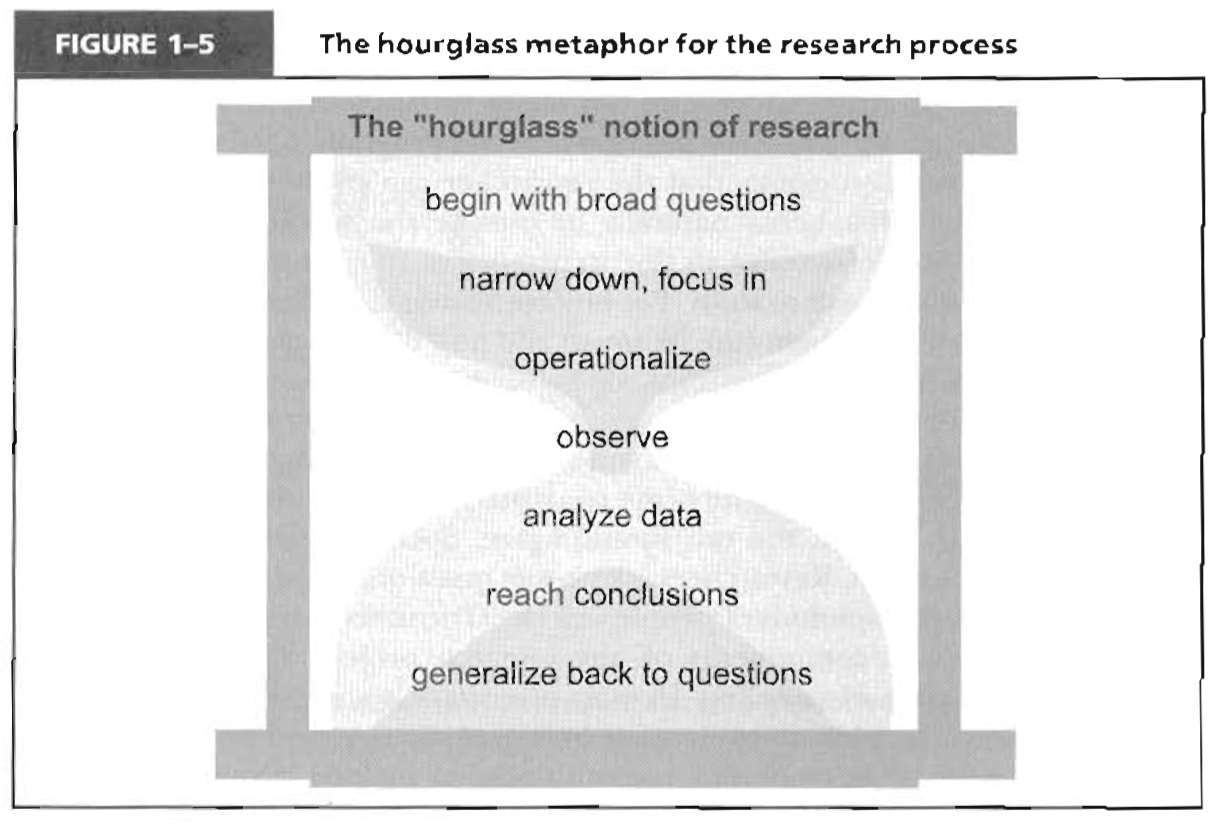
- Hourglass shape – broad area of interest to measurement and observation to generalize back to question
- 1-2a Structure of research
- Components of a study
- Research problem
- Research question
- Program (cause)
- Units
- Outcomes (effects)
- Design
- 1-2b Deduction and Induction
- Deductive
- More general to more specific
- Top-down approach
- Inductive
- From specific to general
- Bottom-up approach
- Deductive
- 1-2c Positivism and Post-Positivism
- Epistemology – philosophy of knowledge
- Methodology – how
- Positivism
- Empiricism – Knowledge as only what could be observed and measured
- Deterministic
- Deductive reasoning
- Post-Positivism
- Theoretical reasoning & experience-based evidence
- Probabilistic
- Critical realism
- External reality
- Never accurate (critical)
- Subjectivist
- World is solely a creation of your mind
- Constructivist
- Reality is a conceptual construction
- Evolutionary epistemology or natural selection theory of knowledge
- Ideal have survival value
- knowledge evolves through a process of variation, selections, and retention (evolution)
- 1-2d Validity
- Best available approximation to the truth of a give proposition, inference, or conclusion
- “Validity of what?”
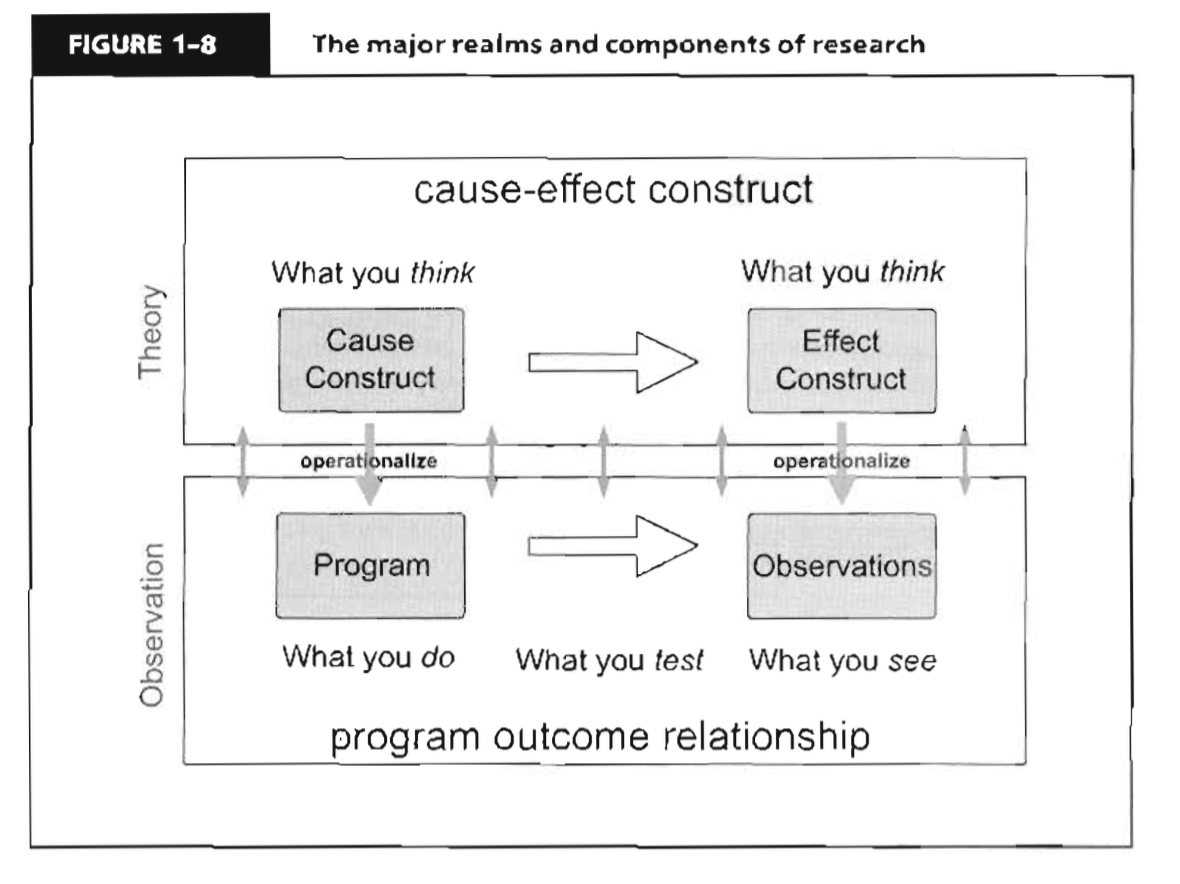
- Four types
- Conclusion
- Is there a relationship between cause and effect?
- Internal
- Is the relationship causal?
- Construct
- Can we generalize to the constructs?
- Cause Construct
- Your theory about the cause in a cause-effect relationship
- Effect Construct
- Your theory what the outcome is in a cause-effect relationship
- External
- Can we generalize to other persons, places, or times?
- Conclusion
- Threat to Validity
- Reasons why your conclusion or inference might be wrong
- Conclusion Validity
- The degree to which your conclusions about relationships in your data are reasonable
- 1-3 Ethics in Research
- 1-3a The Language of Ethics
- Voluntary participation
- Make sure there is no coercion to participate
- Informed consent
- Information about procedures and risks involved
- Confidentiality
- Their personal/individual information or identity will not be released beyond the scope of the study
- Institutional Review Board (IRB)
- Panel who reviews research proposals with respect to ethical implications
- Voluntary participation
- 1-3a The Language of Ethics
- 1-4 Conceptualizating
- Concept Mapping
- 2D graphs of a group’s ideas – used to develop conceptual framework for a research project
- 1-4a Problem formulation
- Comes from practical problems in the field
- Request for Proposals (RFP)
- Feasibility
- Literature Review
- 1-4b Concept mapping
- Pictorial representation of ideas
- Steps:
- Preparation
- Generation
- Structuring
- Representation
- Interpretation
- Utilization
- 1-4c Logic models
- Concept Mapping
Nathan, M., & Alibali, M. (2010). Learning sciences. WIREs Cognitive Science. DOI: 10.1002/wcs.54